Real Time Location System
An assessment of worksites across Australia reveals that safety is the most important element of any project. Yet there are still many injuries and deaths across worksites each year, especially in the agriculture, warehousing, and construction sectors. These facts allude to the fact that there is not enough being done to mitigate the risks at work and we need to start utilizing technology to eliminate some of these hazards. Our project capitalizes on the need for drastic safety measures on certain worksites by utilizing very powerful low-cost technology to create a precise real-time tracking system equipped with an alert system.
The system employs Ultra-wide Band (UWB) technology which as the name suggests transmits information over a large bandwidth. It operates at a low power spectral density which limits signal interference. UWB generates short pulses which allow for precise measuring which enables real-time location tracking down to less than 30cm.
Using UWB as the core of our project we designed ‘tags’ that are equipped with a UWB module (DWM1000), Wi-Fi module (ESP8266) and accompanying circuitry allowing for efficient low-power use. This device will be able to alert the workers when they are deemed to have entered unsafe areas. Alerts are sent through Wi-Fi (ESP8266) to remind workers of the hazards around them, as they come within a determined distance that we deem could be a hazard to the workers. This is indicated as an LED turning on but in the future will utilize vibration and a speaker as well in order to guarantee the worker is alerted to the upcoming hazard.

Project Scope
The purpose of this project is to design an alert system that can:
Detect the location of dangerous machinery or moving parts over various landscapes.
Alert respective personnel when they are approaching a dangerous zone, and
Lasts for a full work day.
Be compact and wearable - won't affect workers' jobs.
RTLS Technology Selection
This project is designed for construction sites and factories where there will be heavy machinery on the move which may obstruct the line-of-sight easily. These factors played a big part in how we were able to choose our technology, some technology just was not versatile enough for these environmental conditions. This project required a very high location tracking accuracy of at least 50 cm to keep the work environments as safe as possible.
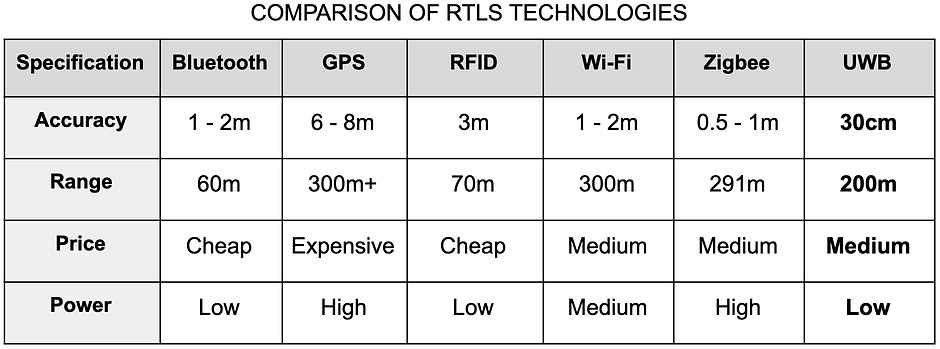
Therefore, after weighing the pros and cons we decided on using the exciting technology of the Ultra-Wide band and using the decawave DWM1000 chip to utilise this frequency band to transmit and receive data. The DWM1000’s range and accuracy is by far the best as illustrated in the table below. With its accuracy dominating the competition at around 30cm with second best being Zigbee at 0.5cm - 1m. Also having a range of 200 m which is more than sufficient for our intentions, we decided that using UWB was the most applicable choice.
DWM1000 also allows for simplicity in how we set up and use the device as it has lots of smart functions purpose built for RTLS. One of these is how the RF design has already been designed for us which simplifies the integration of the device. Its low cost and low power consumption made it perfect for our project as we have a limited budget and our device is battery powered and it is required to run a full work day. This low power consumption also reduces the need to replace batteries which will lower the overall cost over the life-time of the system.
System Architecture
The figure below shows the top-level system architecture abstraction prototype and 2D map of the RTLS system.
The system uses three anchors to set the 2D mapping area of the worksite or factory. One of the anchors (also known as Main Anchor) is connected to the main console i.e. laptop/computer. When a tag is connected to the system, it will first pair itself up with each anchor. Once the tag has been paired up with each anchor, ranging is carried out. The ranging result will be sent to the main anchor to calculate the relative position of the tag.
Once the position of the tag has been determined, the location of the tag is then sent to the main console through the USB port. The main console will display the location of the tag in a 2D map and decides whether to send an alert to the tag.



Hardware
Prototype 1
For our first prototype, we have chosen to use Arduino Pro-mini 3.3V along with FTDI and DWM1000. Arduino Pro-mini is chosen as our microcontroller due to the following reasons:
Our research on similar applications shows that DWM1000 works well with Arduino Pro-mini and Arduino Uno.
Pro-mini is comparably cheaper than other microcontrollers such as Arduino UNO.
It has a fixed internal power regulator of either 3.3V or 5V. In this case, we choose 3.3V as DWM1000 operates between 2.8V to 3.6V